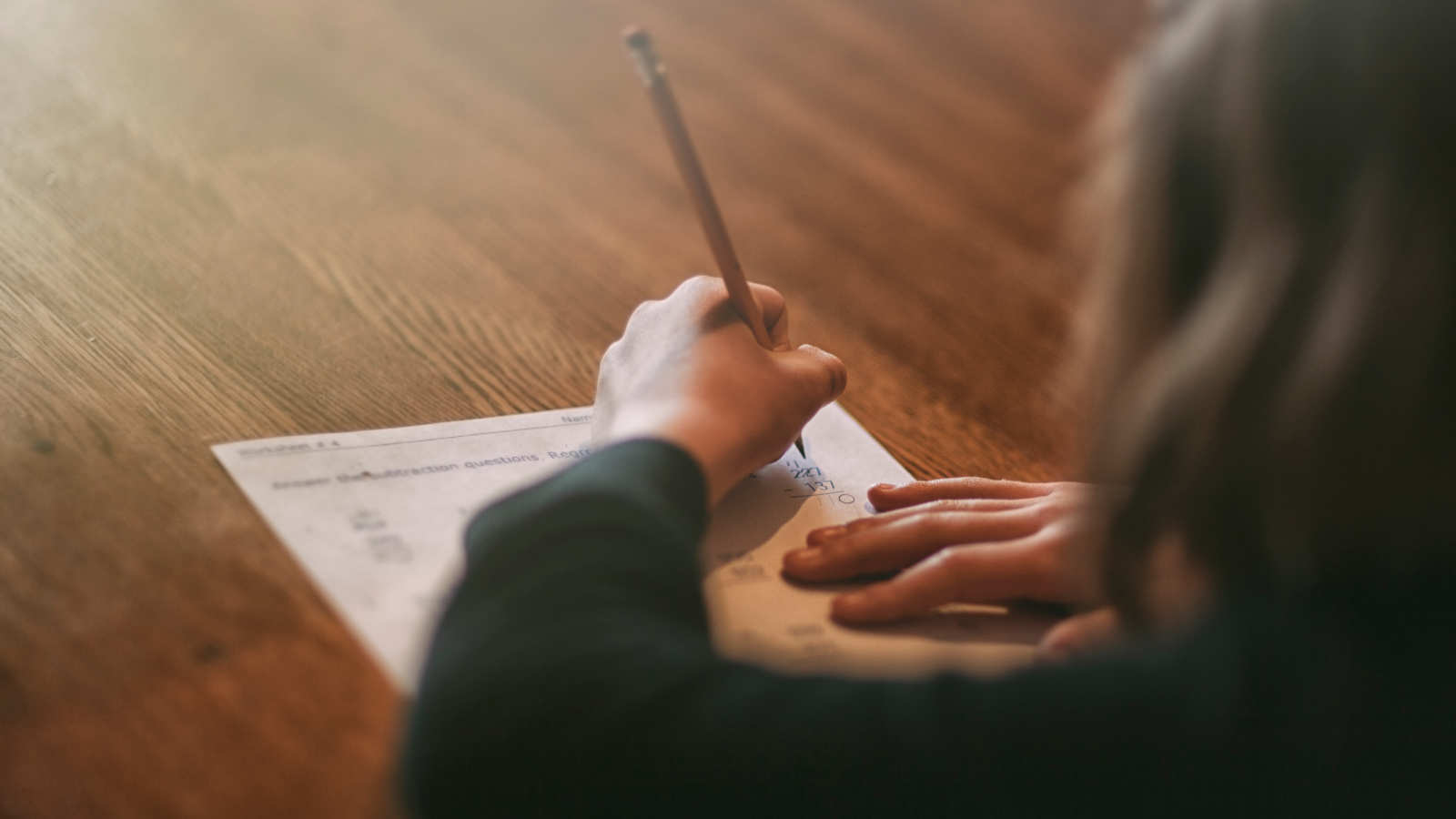
Classroom teaching may be driving a gender gap in math performance, and the effect starts from the moment children begin school, a new study finds.
The study, published July 11 in the journal Nature, included data on the math skills of more than 2.5 million first-grade children in France. It revealed that, while girls and boys started school with a similar level of math skills, within four months, boys performed significantly better than girls. That gap quadrupled in size by the end of the first year of formal education.
Gender gaps in math performance have been documented the world over, and the origin of this disparity has long been blamed on supposedly inherent differences between the genders — “boys are better at math” and “girls are better at language” — that are actually just stereotypes without scientific backing.
But the new study — and previous studies conducted in the U.S. — throw a wrench in those ideas, and instead suggest that something about formal math education spurs the gap to form.
“I was very surprised, not by the fact that there was a gender gap, but that it emerges at the time when formal math instruction in school begins,” study coauthor Elizabeth Spelke, a professor of psychology at Harvard University, told Live Science.
Formal education widens gaps
The new study leveraged an initiative by the French Ministry of Education to boost national math standards, which was launched after several years of disappointing performances in international assessments and uncovered the disturbing extent of the math skills gender gap in the country.
Related: Is there really a difference between male and female brains? Emerging science is revealing the answer.
With the aid of cognitive scientists and educators, the French government implemented a universal program of testing for all French children to help teachers better understand the needs of each class and inform updated national standards. Since 2018, every child’s math and language skills have been assessed upon entry into first grade, the first mandatory year of schooling in France. They were tested again after four months of formal education and then after one complete year of learning.
These tests revealed no notable differences between girls’ and boys’ mathematical ability when starting school. However, within four months, a sizable gap opened up between them, placing boys ahead, and that gap only grew as schooling progressed, suggesting that classroom activities had created the disparity, the study authors proposed.
Spelke and her team’s analysis covered four national cohorts whose data were collected between 2018 and 2022, and included demographic data to probe the role of external social factors — such as family structure and socioeconomic status (SES) — on school performance. But they found that the emergence of the math gender gap was universal and transcended every parameter investigated: regardless of SES, family structure or type of school, on average, boys performed substantially better in the third assessment than did girls.
This bolstered the hypothesis that an aspect of the schooling itself was to blame. And that idea was further supported by data from the cohort impacted by COVID-related school closures, Spelke added.
“When schools were closed during the pandemic, the gender gap got narrower and then they reopened and it got bigger again,” she said. “So there are lots of reasons to think that the gender gap is linked in some way that we don’t understand to the onset and progress of formal math instruction.”
Causes of the math performance gap
For Jenefer Golding, a pedagogy specialist at University College London who was not involved in the study, the research raises worrying questions about attitudes or behaviors in the classroom that could be creating this disparity.
“Gendered patterns are widespread but they’re not inevitable,” Golding told Live Science. “It’s about equity of opportunity. We need to be quite sure that we’re not putting avoidable obstacles in the way of young people who might thrive in these fields.” However, separating these educational factors from possible social or biological contributors remains a complex issue, she said.
As a purely observational study, the research does not allow any firm conclusions to be drawn about why this gender gap becomes so pronounced upon starting school. But the alarming findings are already prompting discussion among educational experts.
Educational analyst Sabine Meinck of the International Association for the Evaluation of Educational Achievement drew on her own research, noting that “our data suggest early gendered patterns in parental engagement, [so] gender stereotypes may begin to take root through early childhood play.”
For example, “parents report engaging girls significantly more in early literacy activities, while boys are more often involved with building blocks and construction toys,” she told Live Science in an email. That may be laying a foundation for how kids engage with reading and math learning in school. These differences in early childhood play have previously correlated with differing levels of scholastic achievement down the line.
The next step requires more research in classrooms, Spelke said, where researchers should gather data to develop interventions that could be useful to students, then test them. “And when we find that something is working, then it can be implemented across the board.”