Quick facts
What it is: The Hubble Ultra Deep Field, revisited by the James Webb Space Telescope
Where it is: Close to the Big Dipper in the night sky
When it was shared: Aug. 1, 2025
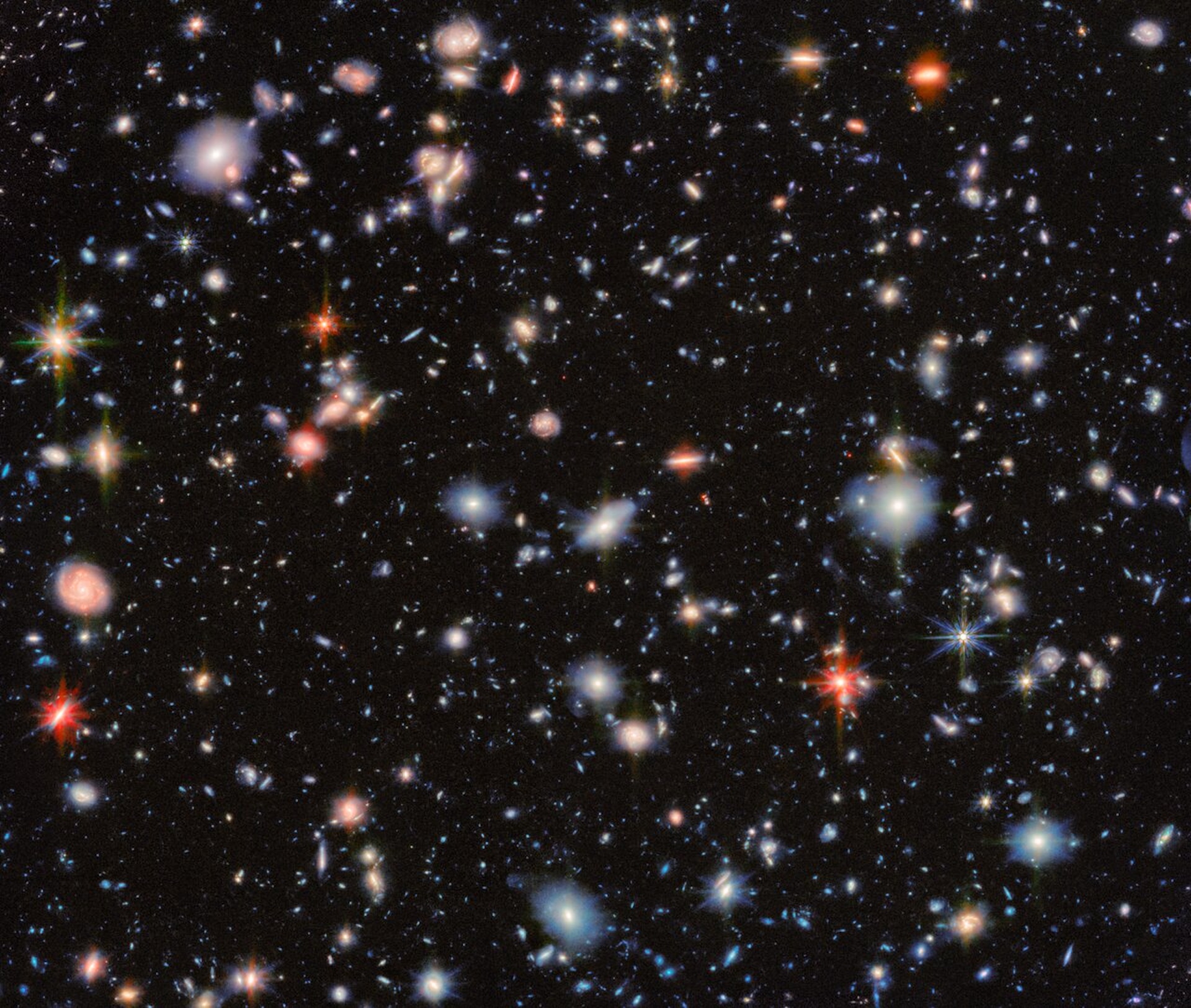
The James Webb Space Telescope‘s (JWST) latest extragalactic survey has revealed fainter and more distant objects than ever before, some dating back to the earliest periods of the universe. But it stands on the shoulders of a giant: When NASA published the Hubble Ultra Deep Field image in 2004, it stunned the world of astronomy. A composite of 800 images from exposures totaling 11 days, the deep image of an otherwise unremarkable part of the night sky revealed nearly 10,000 galaxies, many among the most distant known.
Now, JWST has observed that same patch of sky with different eyes — and found 2,500 more objects. Crucially, they’re even more distant.
JWST’s new take on the Hubble Ultra Deep Field, named the MIRI Deep Imaging Survey (MIDIS), is the deepest-ever mid-infrared image of that part of the night sky.
The extraordinary new image is the result of nearly 100 hours of observing time using the space observatory’s Mid-Infrared Instrument (MIRI) and Near-Infrared Camera (NIRCam). It includes hundreds of extremely red galaxies, some of which may date back to less than a billion years after the Big Bang.
Related: 42 jaw-dropping James Webb Space Telescope images
At the core of the composite image is one ultralong exposure. Using just one of MIRI’s filters, JWST took an exposure of the night sky for 41 hours — the longest single-filter observation it has performed of an extragalactic field to date. The plan was to capture galaxies in mid-infrared light — something neither Hubble nor human eyes can detect — which also revealed previously unseen regions of dust and old, red stars.
Capturing light in wavelengths beyond the capabilities of human vision always brings a problem: How can we even begin to look at it? Processing such images requires filters that assign a different color to each different wavelength of light. In this image, galaxies rich in dust and star-forming activity are orange and red, extremely distant compact galaxies are greenish, and galaxies bright in the near-infrared are blue and cyan.
Researchers described the image in a paper in the journal Astronomy & Astrophysics, along with a slider tool, a pan video and a transition video with the Hubble Ultra Deep Field for comparison.
For more sublime space images, check out our Space Photo of the Week archives.