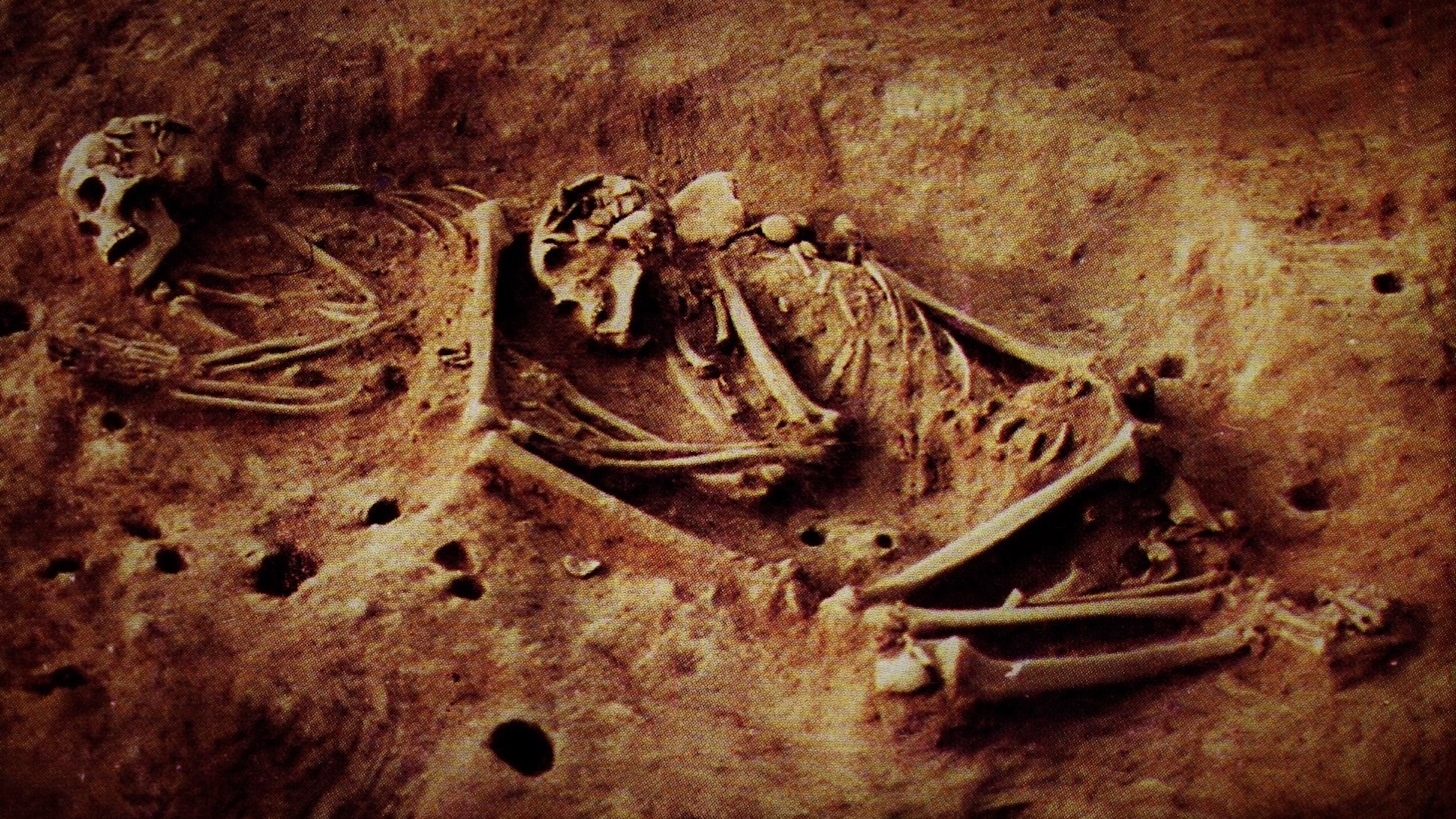
A new analysis of ancient DNA from hunter-gatherers who lived millennia to centuries ago has revealed a previously unknown genetic lineage of humans who lived in what is now Colombia.
People of this lineage lived near present-day Bogotá around 6,000 years ago but disappeared around 4,000 years later, according to a study published May 28 in the journal Science Advances. The findings could shed light on major cultural changes that occurred during that time.
It’s thought that the first Americans journeyed along the Bering Land Bridge from Asia during the last ice age and arrived in North America at least 23,000 years ago, according to trackways found at White Sands National Park in New Mexico. It’s still debated when the first people arrived in South America, but there’s evidence of people at the site of Monte Verde II, in Chile, from 14,550 years ago.
Some of the early Indigenous people who reached South America settled in the Altiplano, a plateau near what is now Bogotá. This region underwent several cultural shifts during the Early and Middle Holocene (11,700 to 4,000 years ago), and researchers already knew about the development of a type of ceramic pottery that emerged during the Herrera period beginning about 2,800 years ago. But how this technology came to the area is still a matter of debate.
To investigate ancient population movements in the region, researchers sequenced genomes using samples from the bones and teeth of 21 skeletons from five archaeological sites in the Altiplano spanning a period of 5,500 years. These included seven genomes from a site known as Checua dating back 6,000 years, nine from the Herrera period around 2,000 years ago, three from the Muisca period, whose remains date to 1,200 to 500 years ago, and two from Guane populations north of Bogotá about 530 years ago.
“These are the first ancient human genomes from Colombia ever to be published,” study co-author Cosimo Posth, a paleogeneticist at the University of Tübingen in Germany, said in a statement.
The genomes from the Checua site belonged to a relatively small group of hunter-gatherers, the team found. Their DNA isn’t particularly similar to that of Indigenous North American groups, nor to any ancient or modern populations in Central or South America. “Our results show that the Checua individuals derive from the earliest population that spread and differentiated across South America very rapidly,” study co-author Kim-Louise Krettek, a doctoral student at the Senckenberg Center for Human Evolution and Paleoenvironment at the University of Tübingen, said in the statement.
But some 4,000 years later, that population had completely vanished. Evidence of their DNA wasn’t present in later groups who inhabited the region, either. “We couldn’t find descendants of these early hunter-gatherers of the Colombian high plains — the genes were not passed on,” Krettek said. “That means in the area around Bogotá there was a complete exchange of the population.”
The findings suggest that cultural changes that occurred at the start of the Herrera period, such as the more widespread use of ceramics, were brought into the region by migrating groups from Central America into South America sometime between 6,000 and 2,000 years ago.
“In addition to technological developments such as ceramics, the people of this second migration probably also brought the Chibchan languages into what is present-day Colombia,” study co-author Andrea Casas-Vargas, a geneticist at the National University of Colombia, said in the statement. “Branches of this language family are still spoken in Central America today.” Chibchan speakers were widespread in the Altiplano at the time of European contact, and genetic markers linked to people who spoke Chibchan languages first appeared there 2,000 years ago.
The Chibchan-related ancestry may have spread and mixed with other groups on multiple occasions. The genetic composition of later Altiplano individuals is more similar to that of pre-Hispanic individuals from Panama than to Indigenous Colombians, suggesting some mixing in Colombia. Ancient remains from Venezuela also carry some Chibchan-related ancestry, though they aren’t as closely linked to ancient Colombians. This suggests the possibility of multiple Chibchan language expansions into South America.
Future studies could involve sequencing more ancient genomes in the Altiplano and nearby regions, the researchers wrote in the study. Such research might help narrow down when Central American populations arrived in the region and how widespread they became.