A grand tomb that may have been built for Alexander the Great’s best friend and bodyguard around 2,300 years ago has an astronomical secret: Its burial chamber is aligned so that sunlight enters it on the winter solstice, a new study proposes.
However, not everyone agrees with this interpretation. Some experts note that the ancient Macedonians used a lunisolar calendar, meaning the winter solstice’s date would have moved from year to year.
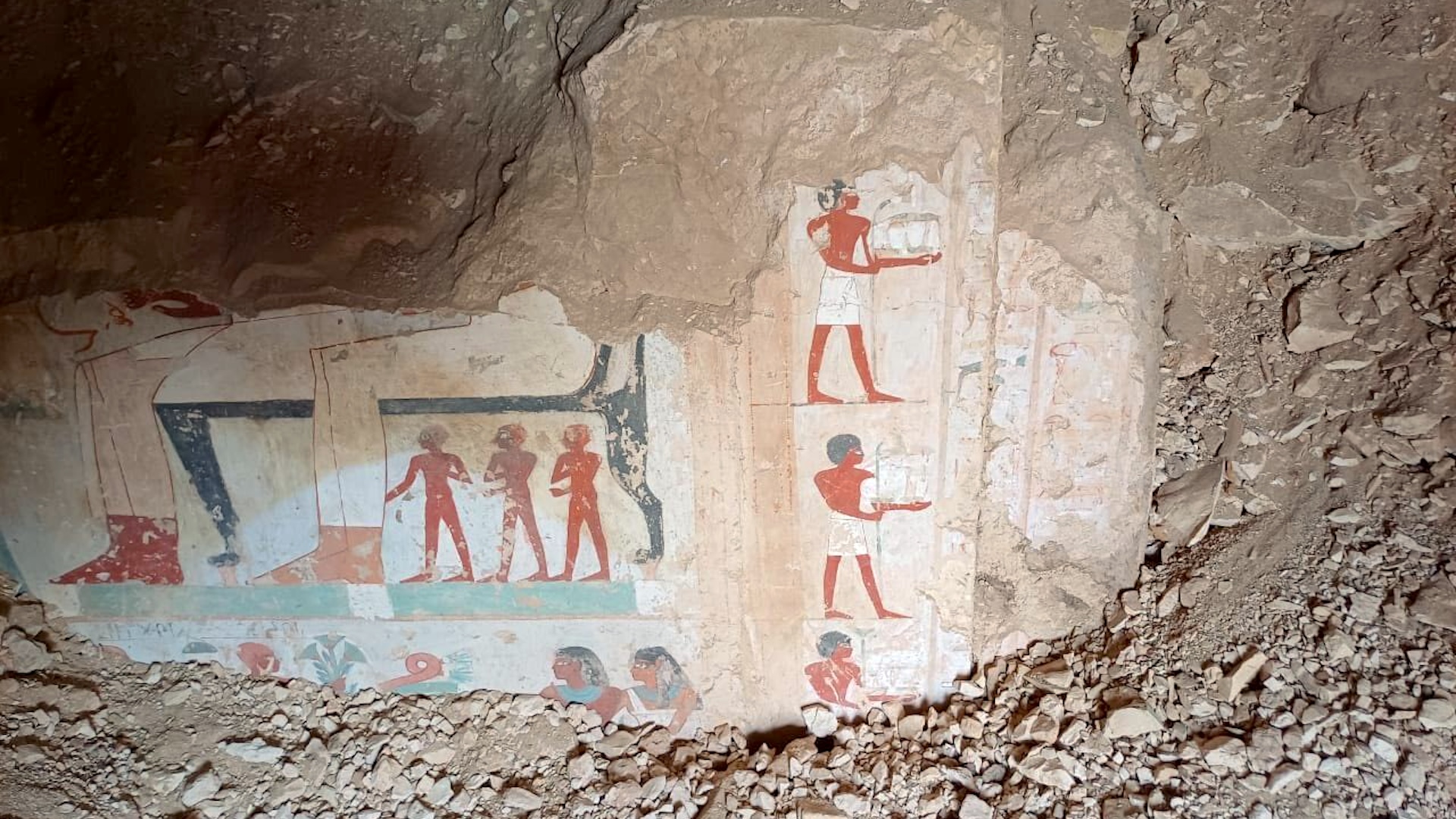
The tomb, now called the Kasta monument (also known as the Kasta tomb or Kasta tumulus), is near the ancient city of Amphipolis in northern Greece. In 2014, archaeologists excavated the tomb’s burial chamber and found the skeletal remains of at least five people. For whom the monument was built is a matter of debate, but Hephaestion (also spelled Haphaestion), whose death in 324 B.C. sent Alexander the Great into severe grief, is considered a leading candidate by some scholars.
In the new study, independent researcher Demetrius Savvides created a 3D model of the tomb and used Stellarium, an astronomical program that tracks how the positions of the sun and stars change over time, to re-create what the sky around the tomb looked like in 300 B.C.
He found that on Dec. 21, the date of the winter solstice, the sun’s light would have fully illuminated the burial chamber between approximately 10 a.m. and 4 p.m. local time, Savvides wrote in a study published May 15 in the Nexus Network Journal.
Related: Was Alexander the Great eaten by sharks? Inside the wild theories for what happened to the iconic ruler’s body.
Sunlight reaches other parts of the monument at different times, he found. Around late July, it touches the entrance. Throughout autumn, the sunlight gradually travels on and near two carved sphinxes and finally passes between them, fully illuminating the burial chamber on the winter solstice.
“It is highly probable that rituals were held within or in close proximity to the Kastas Monument, particularly on and around the winter solstice,” Savvides told Live Science in an email.
Initially, when the tomb was being built, it had no orientation to the winter solstice. But during its construction, the design was changed to create the solstice alignment, Savvides wrote in the paper. An alignment like this would have symbolized “themes of renewal, life, and cosmic order,” Savvides said in the email.
These themes are also seen in the tomb decoration, which shows a mosaic of Persephone, a goddess of vegetation and agriculture who is also queen of the underworld, Savvides noted. In addition, the tomb has a possible depiction of Cybele, a goddess who was associated with birth and fertility and was married to Attis, a god also associated with vegetation who died and was resurrected.
A link to Alexander’s tomb?
One interesting question this research raises is whether Alexander the Great’s tomb, which was constructed in Alexandria, had a burial chamber with an alignment like this, Savvides said. “The use of solar illumination and a consistent geometric design aligns with Hellenistic traditions where rulers, like Alexander the Great, used solar symbolism to reinforce their authority,” Savvides said.
“If we were to locate Alexander’s tomb, it might resemble the Kastas Monument,” Savvides said. Alexander’s tomb has never been found and might be underwater or underneath Alexandria.
Juan de Lara, a researcher at the University of Oxford who has investigated the alignments of ancient Greek buildings, had mixed reactions to the research.
“I think it’s great that scholars are asking these questions and using this technology to generate new ideas. In the case of the tomb, the researcher presented daring hypotheses,” de Lara told Live Science in an email. “However, we must remember to be very careful when relating such findings to ‘solar’ events, as the Macedonians used a lunisolar calendar — meaning that the dates shifted from year to year.”
In other words, their winter solstice would have fallen on a different day each year, meaning this day of illumination might have been difficult to observe annually as the day changed. Additionally, de Lara noted that northern Greece is very cloudy in the winter and the effect may not have been noticeable.
Alexander the Great quiz: How well do you know the famous king and conqueror from the ancient world?