A second “new star” has unexpectedly appeared in the night sky, less than two weeks after a near-identical point of light first burst into view without warning.
These never-before-seen “stars” are made of light coming from rare stellar explosions known as classical novas. Scientists believe this may be the first time in recorded history that more than one of these luminous outbursts have been visible with the naked eye at the same time.
The first nova, dubbed V462 Lupi, was initially spotted June 12 shining in the Lupus constellation, after its progenitor star suddenly became more than 3 million times brighter than normal. Then, on June 25, multiple astronomers detected another nova, dubbed V572 Velorum, within the Vela constellation, according to EarthSky.org. Astronomers normally expect to see a classical nova once a year at most, and more than one of these explosions shining simultaneously is almost unheard of.
“This is without question an extremely rare event, if not an historical one,” Stephen O’Meara, an astronomer and author who has been scouring historical records for similar examples, told Spaceweather.com. “I have yet to find an occurrence of two simultaneous nova appearing at the same time.”
The last time we came close to simultaneous novas visible to the naked eye was in 1936, when V630 Sgr and V368 Aql were spotted within a few weeks of one another, O’Meara added. However, “they were not at maximum brightness at the same time.”
Related: Nearly 900 years ago, astronomers spotted a strange, bright light in the sky. We finally know what caused it.
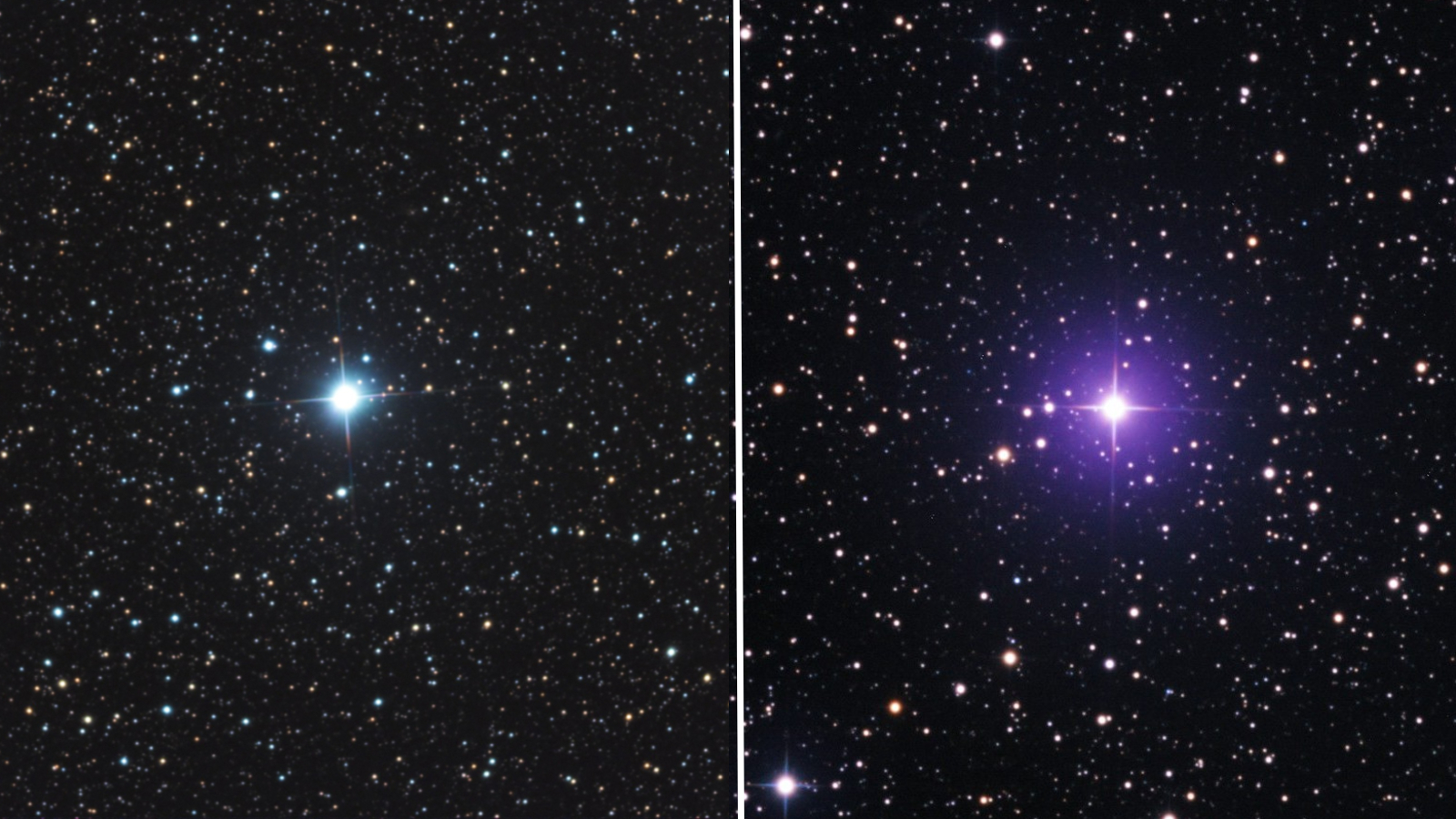
V462 Lupi’s brightness peaked on June 20, when it reached an apparent magnitude of +5.5. The star has since dimmed slightly but remains above the +6 magnitude threshold for naked eye visibility. V572 Velorum is even brighter, peaking at +4.8 on June 27. (A smaller magnitude signifies a brighter object; for example, the moon has an apparent magnitude of -12.7.)
Astrophotographer Eliot Herman snapped the novas using a remotely operated camera in Chile (see above). V572 Velorum, which was photographed on June 27, shines with brilliant blue-white light, while V462 Lupi has a purple hue in an image captured on June 26. Novas gradually turn red before disappearing because the longer blue-colored wavelengths of light fade from view first.
Both the Lupus and Vela constellations are in the southern sky, making the new novas easier to spot from the Southern Hemisphere. However, V462 Lupi can be seen from North America, just after sunset and close to the southern horizon. Vela can sometimes be seen from the southern parts of North America, including Mexico, California and Texas, meaning some people in these regions could spot V572 Velorum for themselves. But it is much less likely.
The objects are technically bright enough to be seen with the naked eye. However, they will be easier to spot if you have a decent telescope or a pair of stargazing binoculars, especially if you are viewing them from the Northern Hemisphere.
Stellar explosions
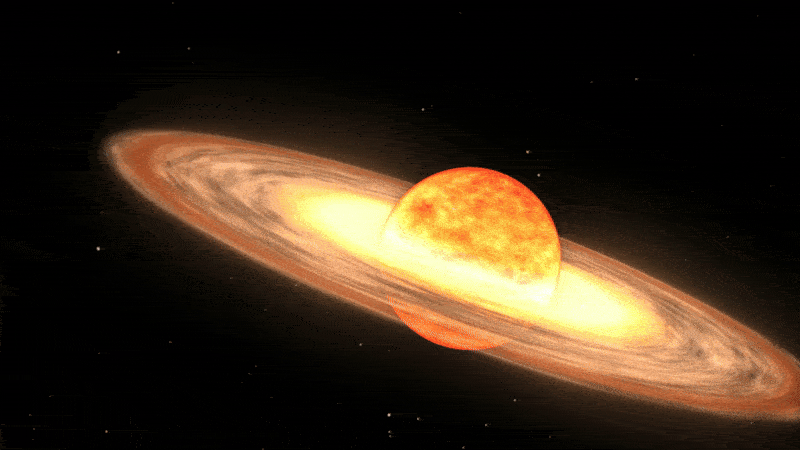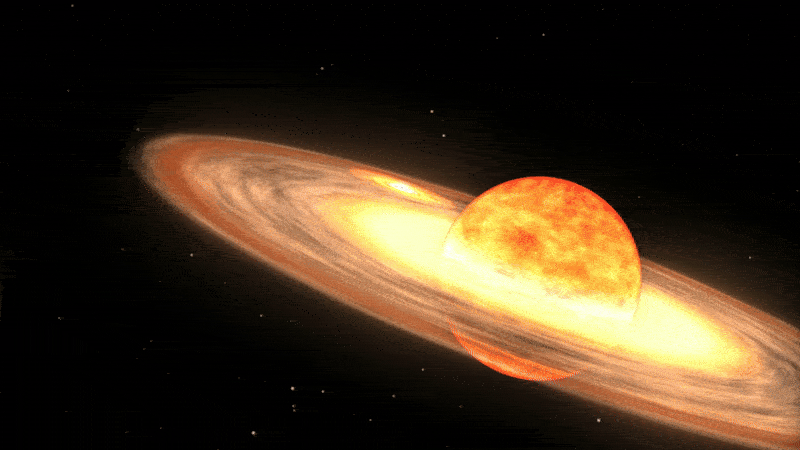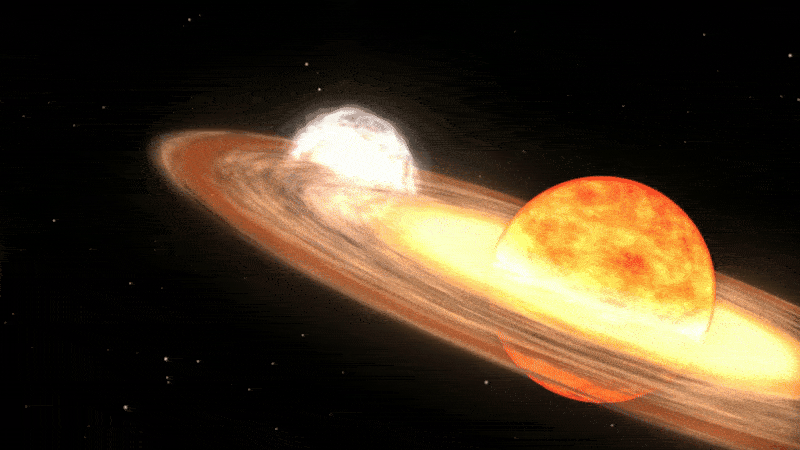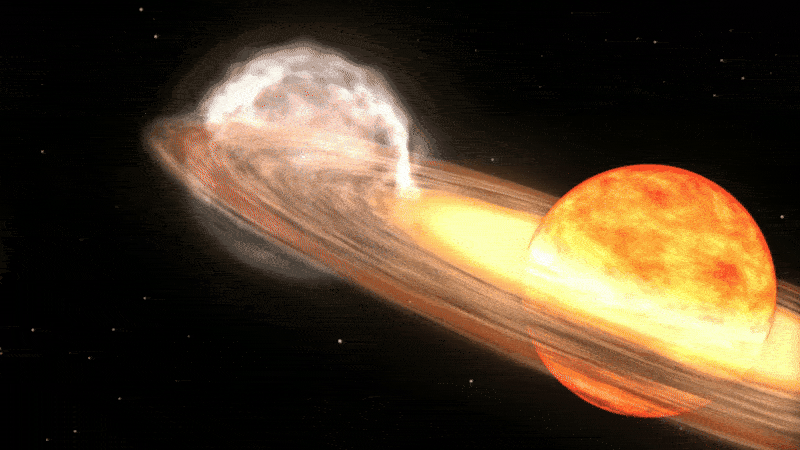
Unlike supernovas, which are so powerful that they completely rip stars apart, a nova only affects the outer layers of a star.
Classical novas, such as V462 Lupi and V572 Velorum, occur in a specific type of binary system, where a more massive white dwarf star is pulling material away from its larger partner. When enough material has been accreted onto the dwarf star’s surface, the pressure builds up and triggers an explosion that burns up most of the stolen gas and shoots pulses of bright light into space, which can sometimes be seen from Earth.
Some novas are recurring events, blowing their top at regular intervals: For example, the long-awaited T Coronae Borealis nova, also known as the “Blaze Star,” lights up our skies roughly every 80 years. However, astronomers have been predicting that the Blaze Star will reappear imminently for the last 15 months, and it is yet to emerge, which shows that it is not an exact science.
As this is the first recorded appearance of V462 Lupi and V572 Velorum, it’s not known if or when they will explode again in the future. Both of them will likely fade from view in the coming weeks.
Constellations quiz: Can you name all the animals, objects and mythological figures hiding in the night sky?














